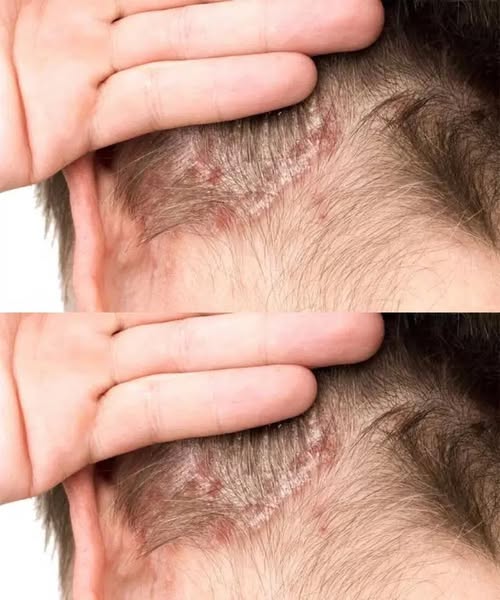
Finding an unusual patch on your child’s scalp can be worrying—especially when you can’t get a doctor’s appointment right away. If you notice a red, scaly, or crusty area on your child’s scalp, there are a few common causes that might explain it.
While only a healthcare professional can provide a diagnosis, understanding the possibilities can help you decide what steps to take next.
Common Causes of Scaly Scalp Patches in Children
1. Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
This is one of the most common causes in children. Despite the name, it’s not caused by worms—it’s a fungal infection.
Signs may include:
Round or irregular scaly patches
Redness and inflammation
Broken hairs or small bald spots
Mild itching
It can spread through shared hats, combs, pillows, or close contact with other children. This condition requires prescription antifungal medication from a doctor.
2. Seborrheic Dermatitis
This condition can appear as greasy, flaky scales on the scalp. In babies, it’s known as cradle cap, but older children can develop it too.
Typical signs:
Yellowish or white flakes
Mild redness
Usually not very itchy
Medicated shampoos often help manage it.
3. Psoriasis
Psoriasis can also affect the scalp.
Symptoms may include:
Thick, silvery scales
Well-defined red patches
Possible itching
It’s a chronic condition that may require medicated treatments.
4. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
If your child already has sensitive skin or eczema elsewhere, the scalp can sometimes be affected.
What You Can Do While Waiting for a Doctor
Since you can’t get an appointment soon, here are safe steps you can take:
✔ Keep the Area Clean
Wash gently with mild shampoo. Avoid harsh scrubbing.
✔ Avoid Sharing Personal Items
Do not share combs, brushes, hats, pillows, or towels.
✔ Try an Over-the-Counter Antifungal Shampoo
If you suspect a fungal cause (like ringworm), you can try shampoos containing:
Ketoconazole
Selenium sulfide
Use 2–3 times per week. This may help reduce spread, but it usually does not fully cure scalp fungal infections without oral medication.
✔ Watch for Warning Signs
Seek urgent care if you notice:
Rapid spreading
Severe swelling
Pus or drainage
Fever
Painful swollen lymph nodes
Is It Contagious?
If it is ringworm (tinea capitis), it is contagious. Until you know for sure:
Avoid close head-to-head contact
Wash bedding in hot water
Clean combs and brushes thoroughly
When to See a Doctor
Even if it improves slightly, scalp infections in children often require prescription treatment. A doctor may:
Examine the scalp
Take a small scraping
Prescribe oral antifungal medication if needed